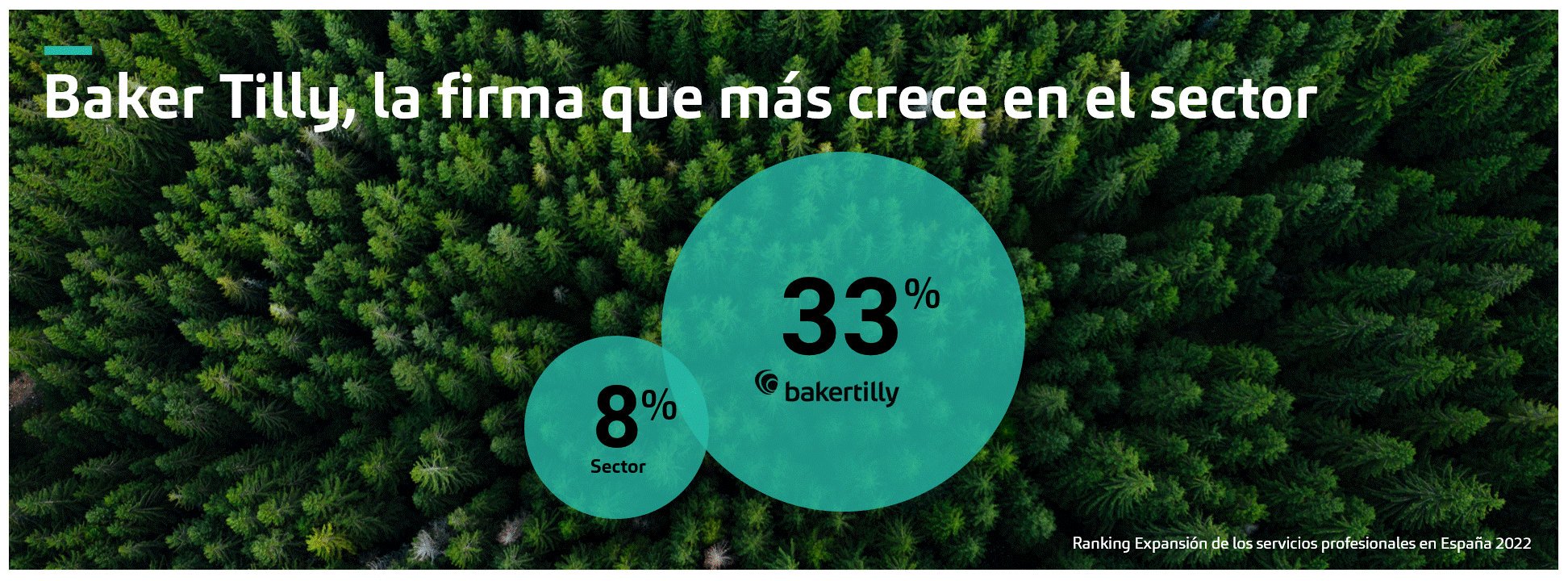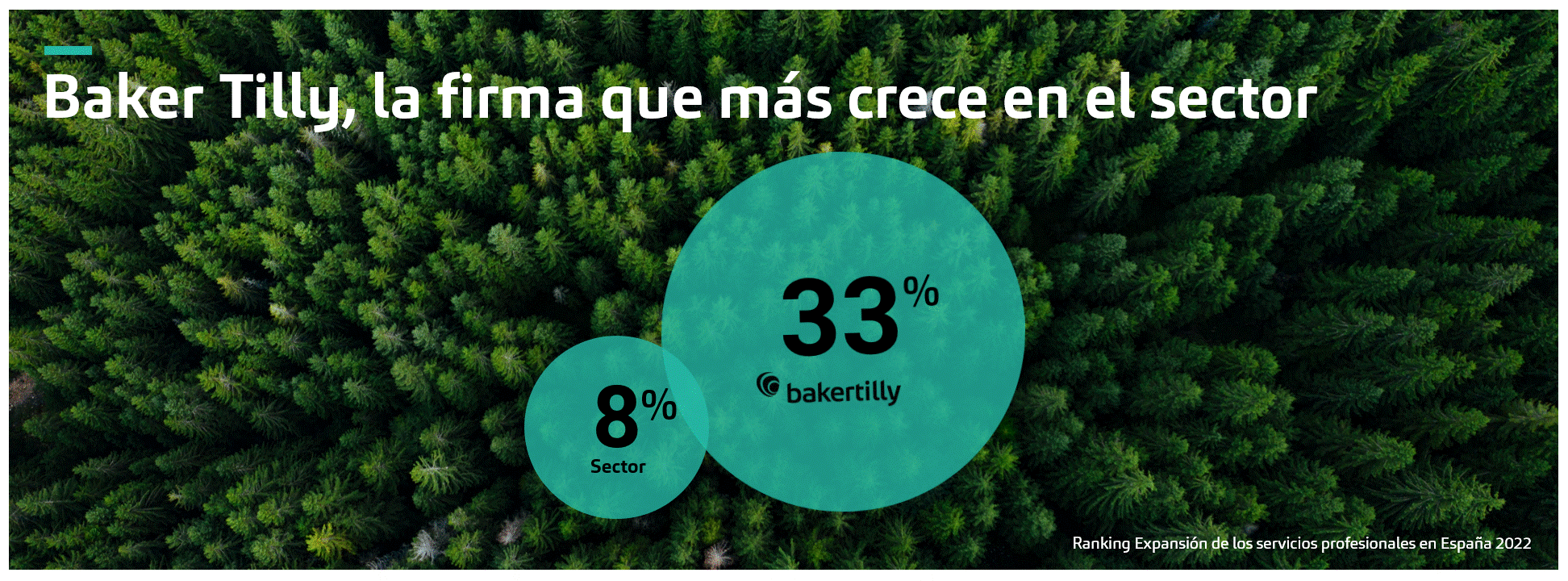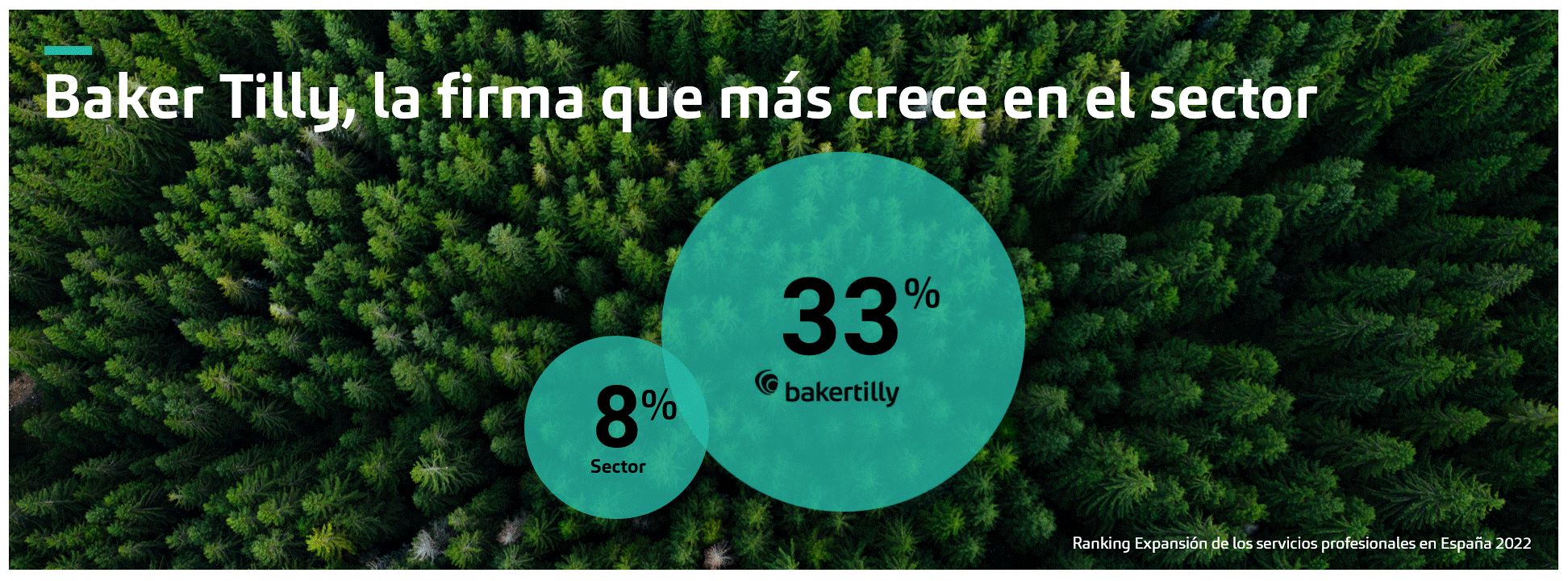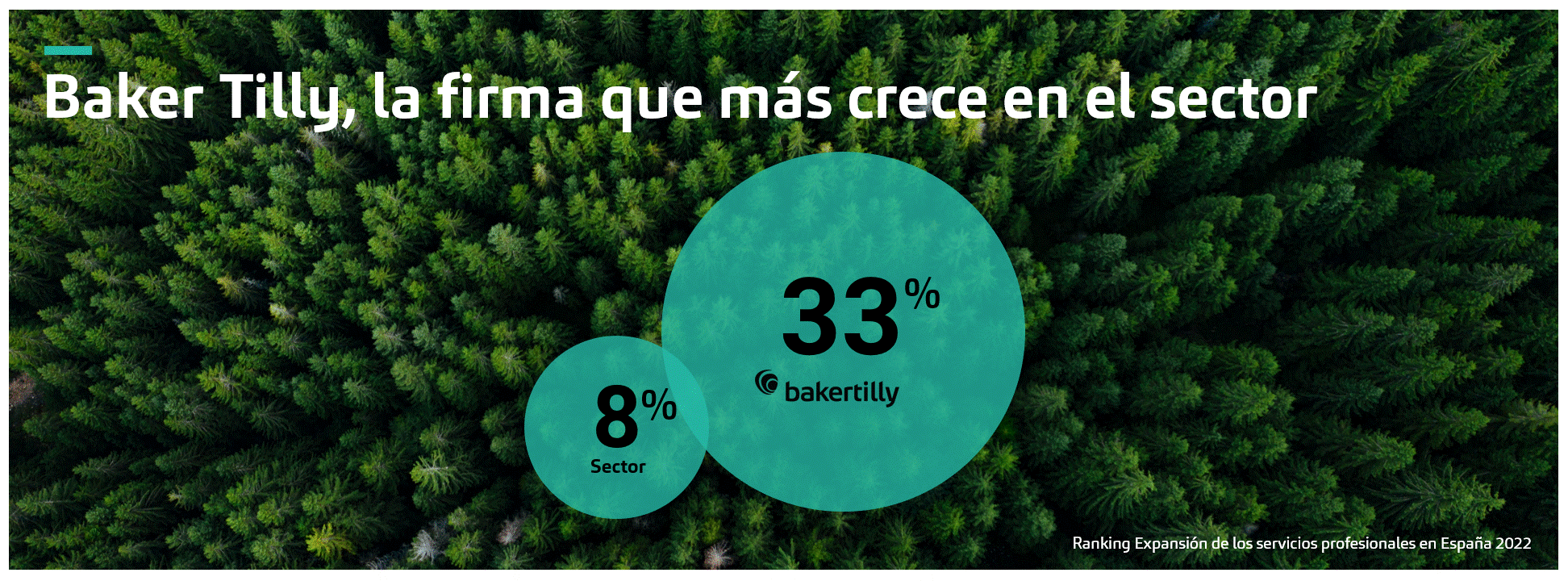
Internal Control and Audit: Key Strategies to Manage Risks in Your Organization
Internal Control and Audit: Key Strategies to Manage Risks in Your Organization
According to COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission), internal control is a process carried out by an entity’s management and staff, designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of objectives in the following categories:
- Effectiveness and efficiency of operations
- Reliability of financial reporting
- Compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and standards
Internal control structure: five key components
The framework is divided into the following core components:
- Control environment
- Risk assessment
- Control activities
- Information and documentation
- Monitoring
Definition of internal control under ISA (Spain) 315 (NIA-ES 315)
The International Standard on Auditing adapted for Spain, ISA (Spain) 315 (NIA-ES 315), defines internal control as a process designed, implemented, and maintained by those charged with governance, management, and staff. This process aims to provide reasonable assurance over the reliability of financial reporting, the efficiency of operations, and compliance with applicable legal requirements.
In this context, the term “controls” refers to any aspect related to one or more components of internal control.
The auditor’s role in analyzing internal control
As part of the audit of the annual accounts, the auditor must:
- Gain knowledge of, understand, and analyze the entity’s internal control procedures.
- Conduct interviews with those charged with governance and management.
- Meet with managers from different departments to compare and validate the information obtained.
Tests of controls: ensuring effectiveness
As part of the audit process, tests of controls are performed to verify that the controls defined in procedure manuals are effective and are actually applied in practice. These tests make it possible to:
- Detect incidents or control failures.
- Assess whether it is necessary to expand audit testing.
- Investigate the causes of errors, distinguishing between isolated and recurring cases.
Benefits of internal control for companies
Internal control helps to:
- Prevent and mitigate risks of error, fraud, or material misstatements in the financial statements.
- Manage the operational risks organizations face in their day-to-day activities.
- Adapt procedures proportionally to the structure and size of each entity.
Having robust internal control systems is key to preventing future issues and ensuring efficient management.